한국의 갯벌Interesting Value of Little Known
- Little known features of Getbol, Korean Tidal Flats is its
unique geo(morpho)logical and bio- & ecological features. -
Getbol, Korean Tidal Flats recognized as a Natural World Heritage, is not only valuable as a ‘biodiversity habitat for endangered species,’ but also shows the on-going geological and geomorphological features, representing major stages of earth's history (criterion ⅷ), and it has outstanding examples representing significant ecological and biological processes in the evolution of communities (criterion ⅸ).
Formation of the Tidal Flats
Generally, tidal flats refer to flat areas formed when they are pushed in from the sea by tidal currents and piled up along the coast. Tidal flat areas, where are widely formed around the world, are located in shallow seas, such as the continental shelf with macrotidal range.
Geo(morpho)logical features of Getbol, Korean Tidal Flats with dynamics
Getbol, Korean Tidal Flats has begun forming 8,500 years ago when the sea level raised after the Last Glacial Maximum. Tidal flat sediments have been currently accumulating at an average of 1mm annually. This is a representative example to clearly show the formation process of Earth’s coastal landform since the Holocene.
-
- A globally unique coastal landform of tidal flats has been created by the dramatic combination of macrotidal range, archipelago, and monsoon climate.
-
In the shallow sea called the Yellow Sea (average water depth 44m), many sediments flow into the sea from the rivers due to concentrated precipitation in summer. This is caused by rapid tidal currents flowing in different directions in summer and winter, spreading to the southwestern coasts of the Korean Peninsula. The rapid tidal currents carrying sediments are weakened when they meet rocky islands, and then diverse habitats surrounding the numerous islands (different types of habitats on the four cardinal points depending on the shape of the island) are forming. (There are few places in the world where such diverse tidal flats have been formed around archipelagic area).
-
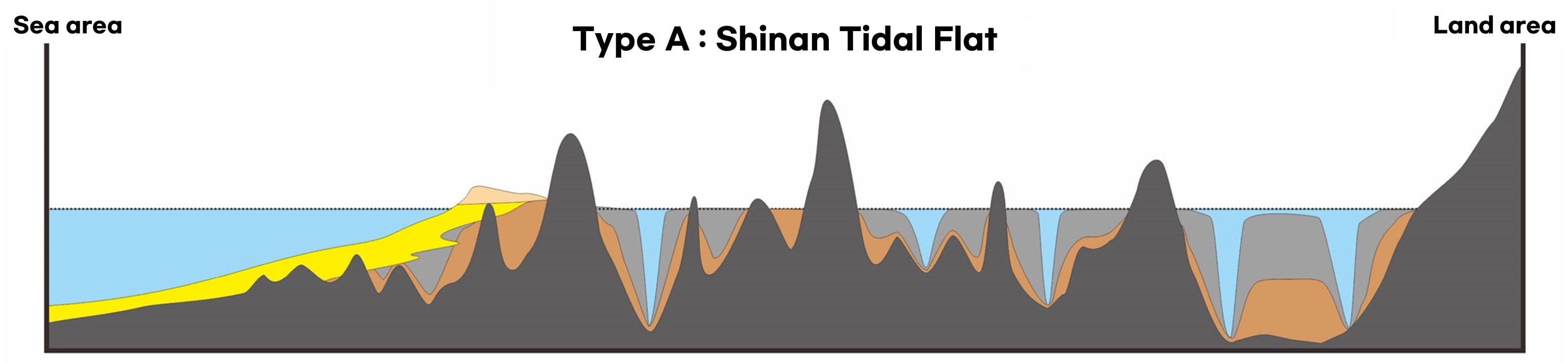
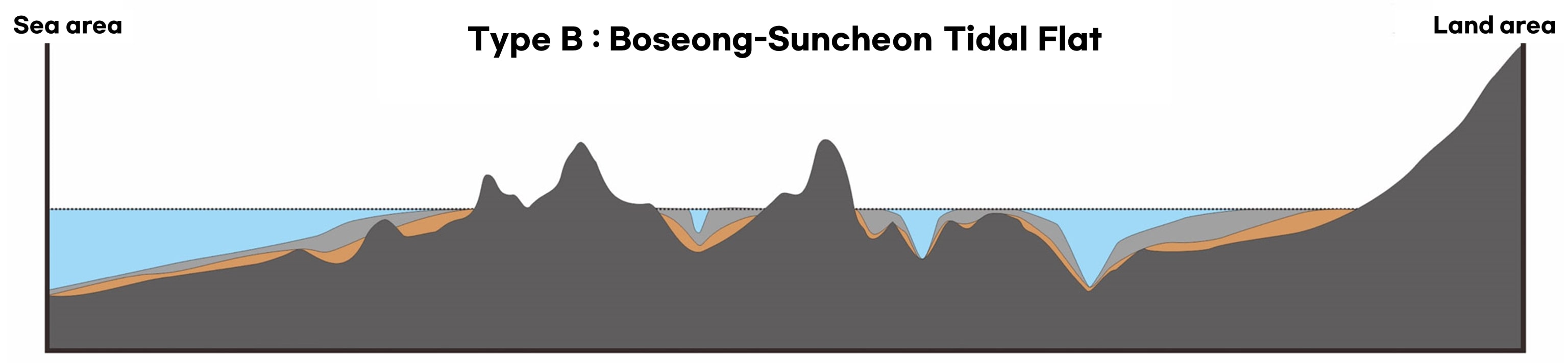
- All types of tidal flats in the world in one place! High geological diversity
-
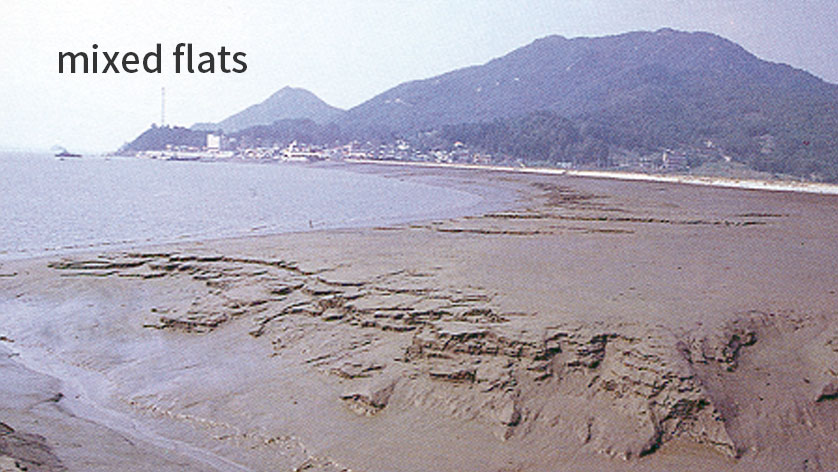
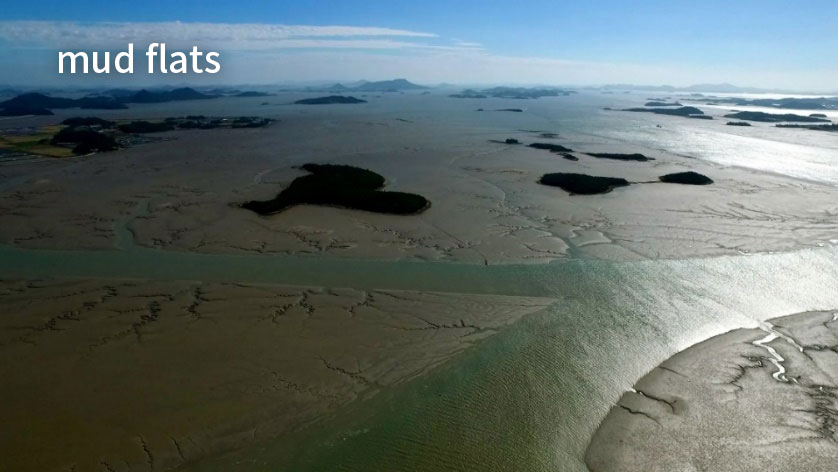
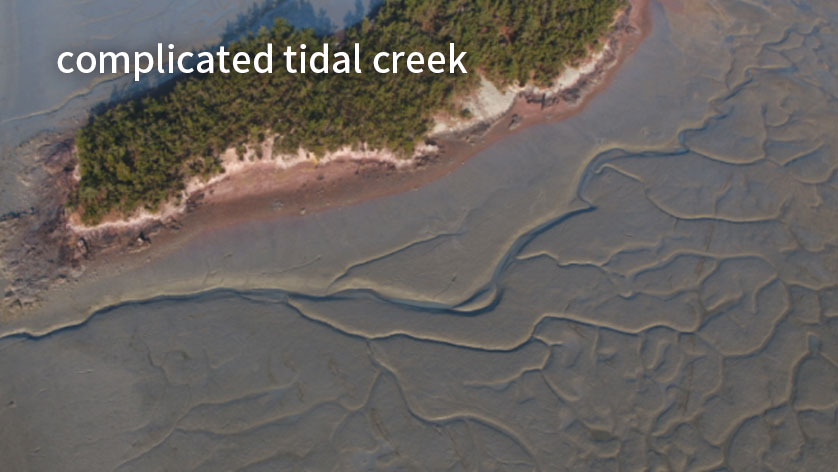
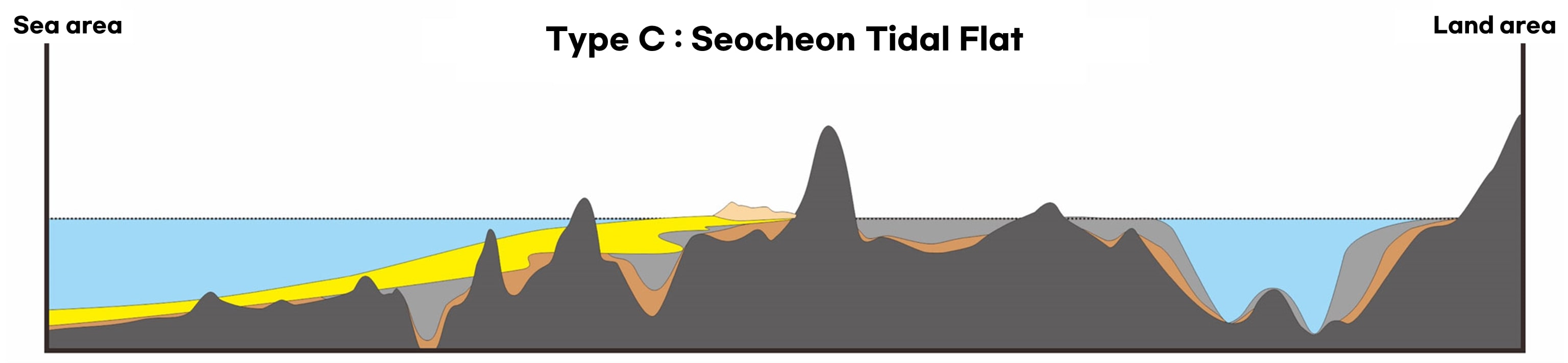
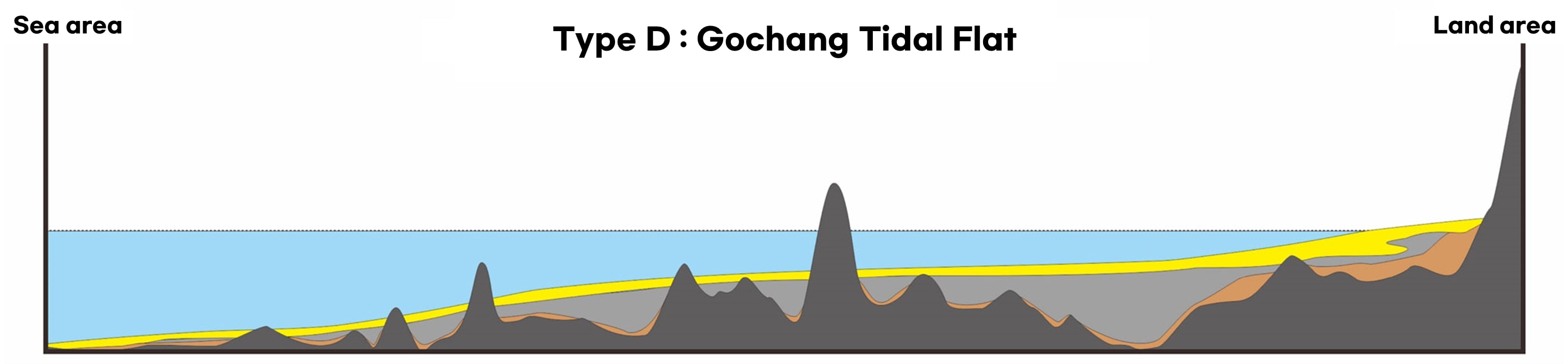
Getbol, Korean Tidal Flats comprises all types of tidal flats that exist on Earth, including a moving island, a chenier, and a unique sediment body with sand bands on a mudflat that is unprecedented in the world, as well as mud flats, sand flats, mixed flats and even rocky tidal flats.
-
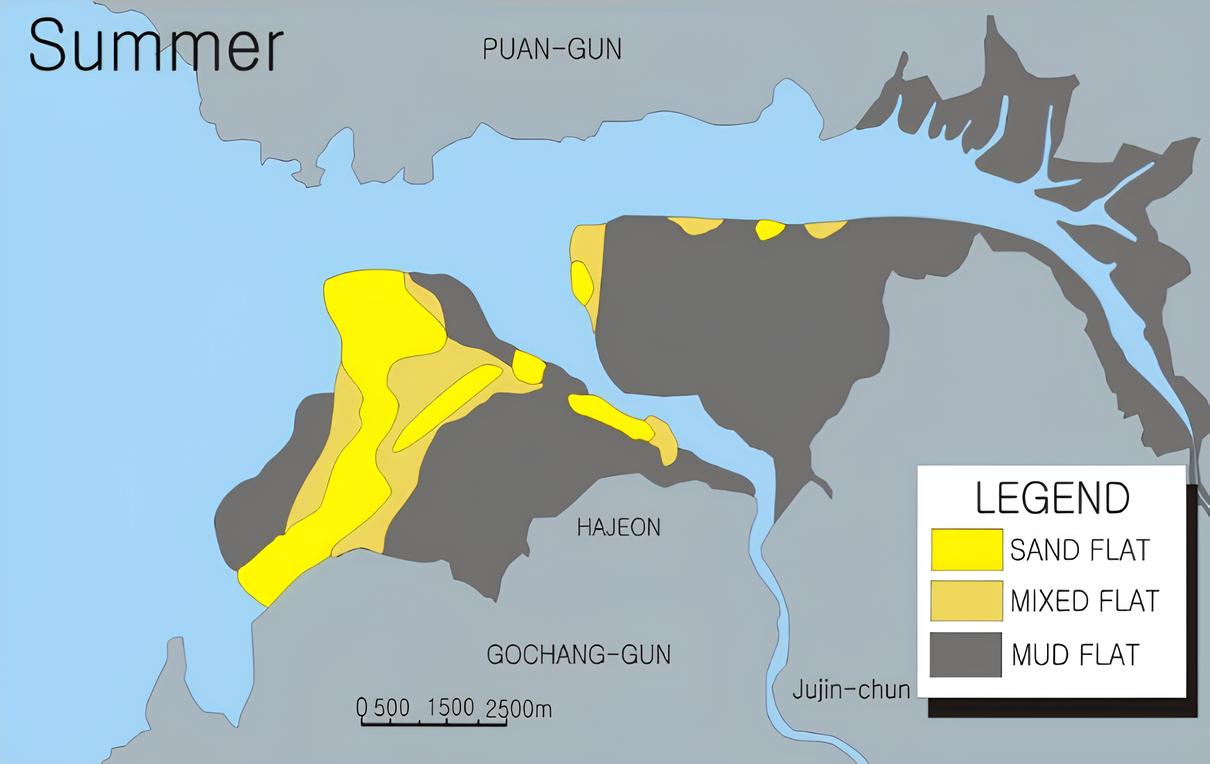
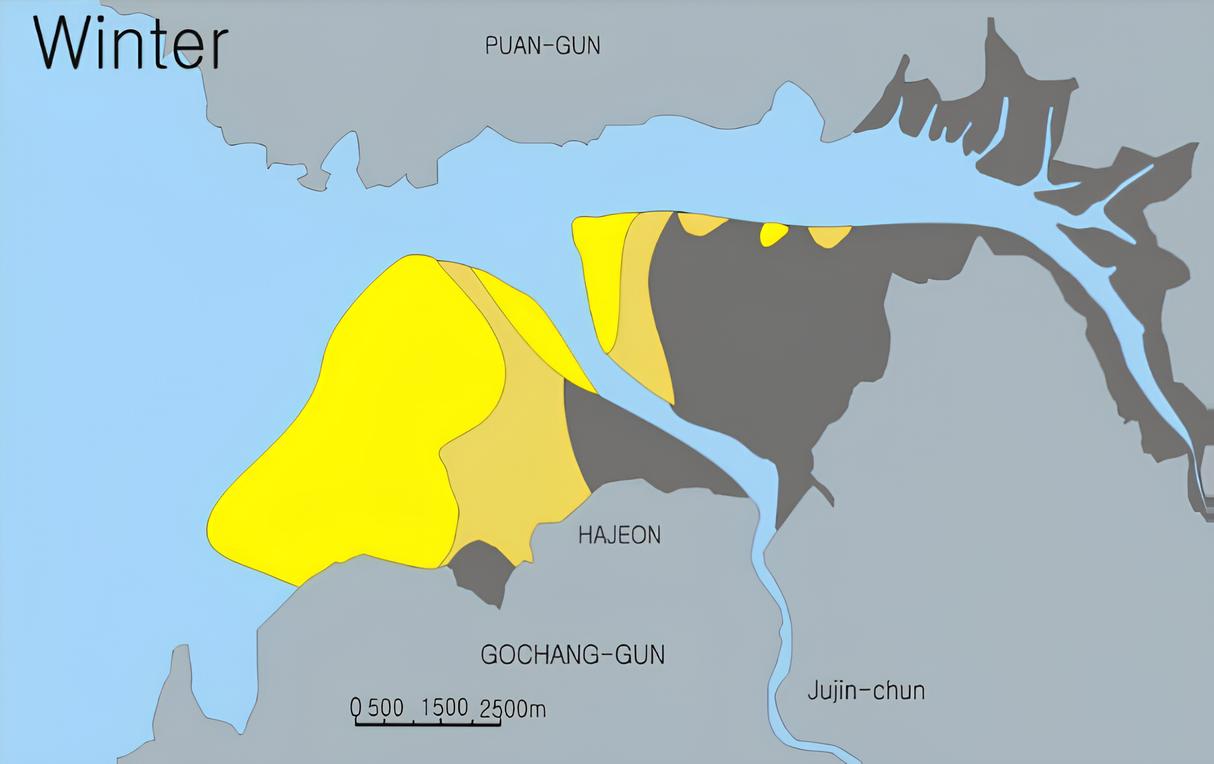
- Tidal flats, changed by the season?!
-
Getbol, Korean Tidal Flats, which is influenced by strong northwest winds in the winter, show seasonal changes. In the summer, tidal flats contain a lot of muddy elements but in the winter contain a lot of sand, even in the same area.
-
- The depth of the mud flat is higher than a 13-floor apartment building?!
-
The island’s inner mud flats, where waves and winds are weakened by rocky islands in the macrotidal range, have a depth of 25m (max. 40m). In particular, Getbol, Korean Tidal Flats shows all the tidal flats’ evolution stages: immature, mature and overmature.
- Holocene mud flats
- Holocene sandy flats&sand dune
- Pre-holocene tidal flat
Bio- and ecological processes
-
- Unique community evolution in each habitat
-
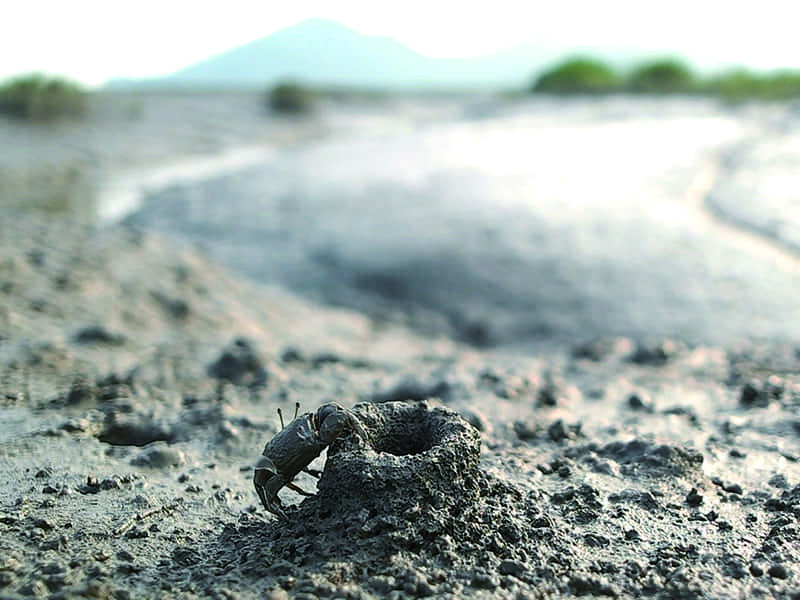
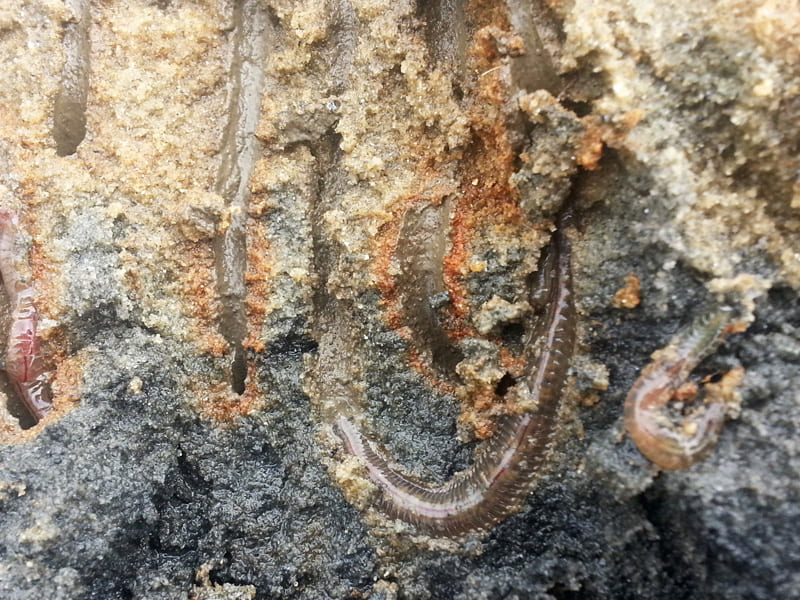
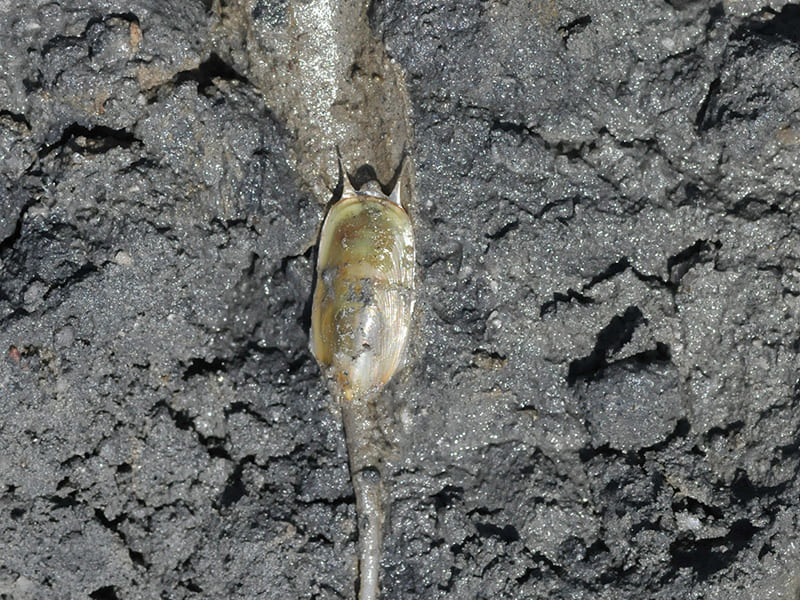
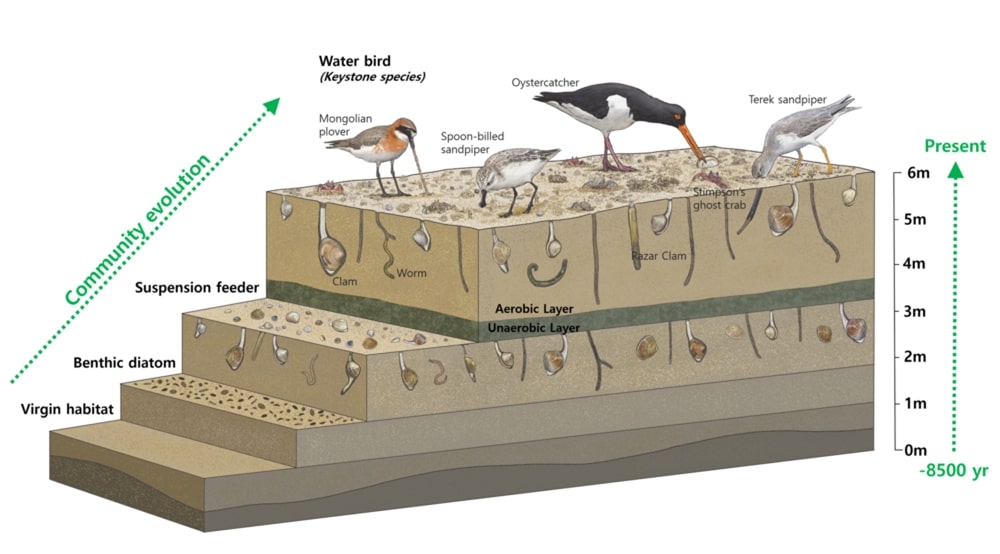
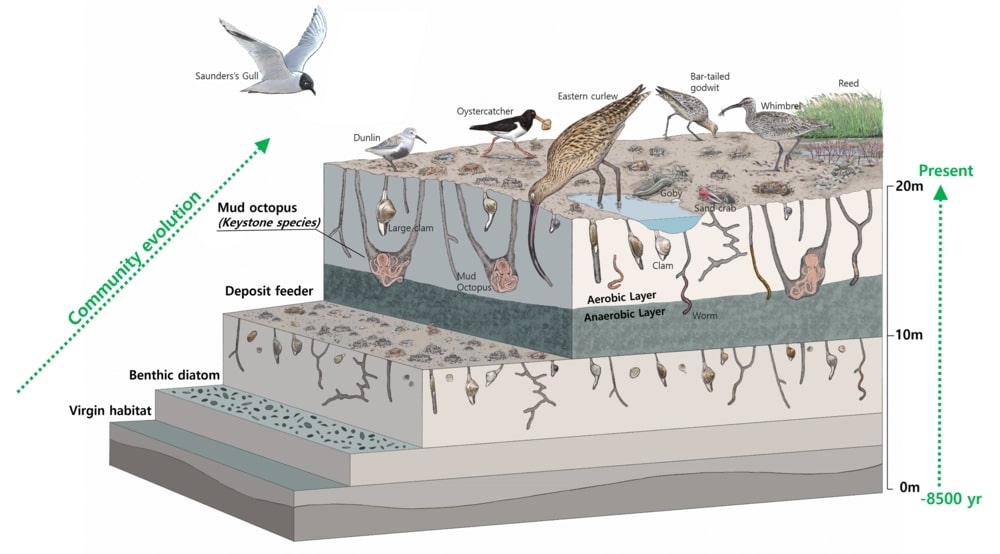
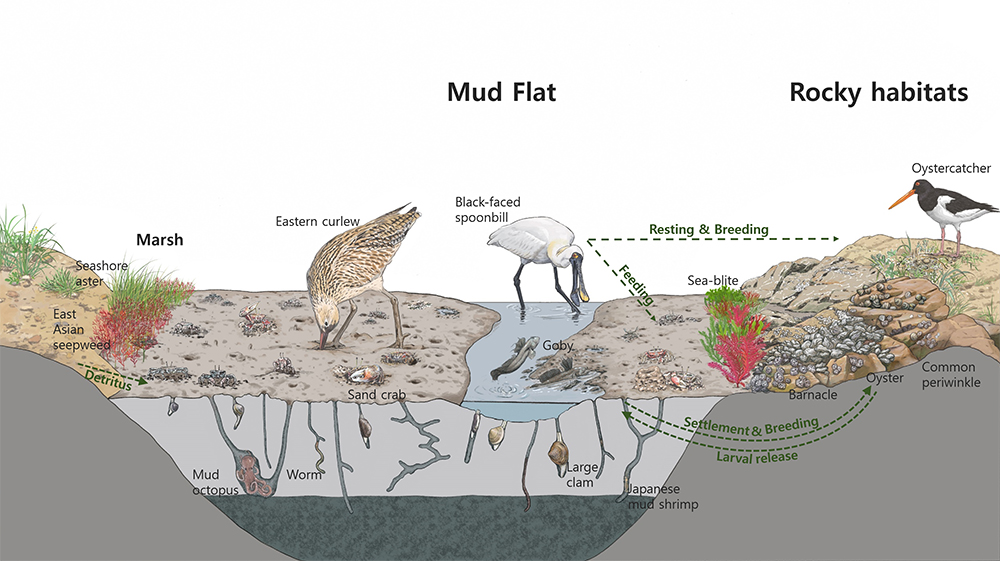
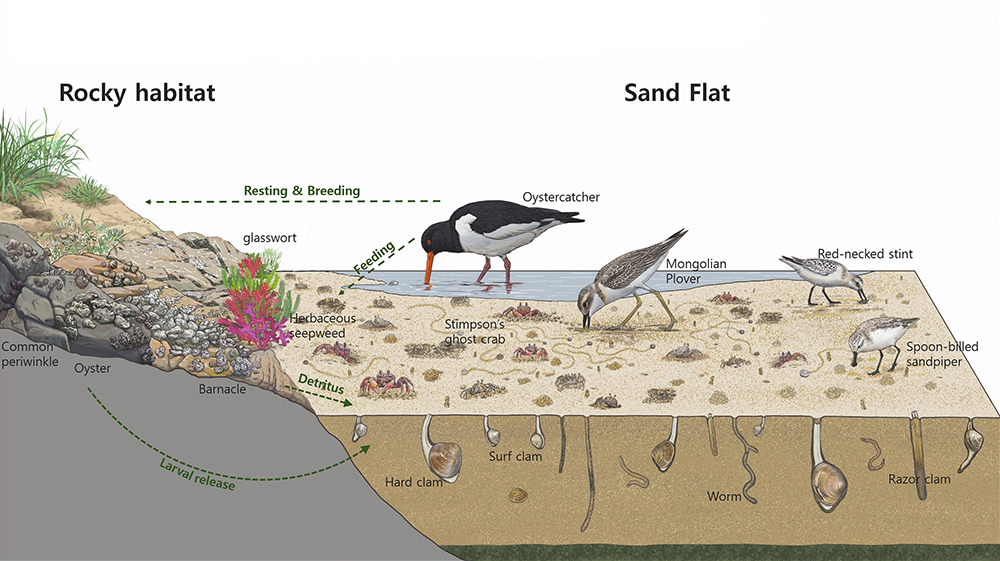
Depending on the types of tidal flats habitat, there are different keystone biological species. Mud flats, made up of very tiny particles, home Japanese Mud Crabs, Mud Fiddler Crabs, and Polychaete Worms that live on organic matters on the sediment’s surface. As well as Mud Octopuses and waterbirds dominate as the top predators. On the other hand, Yellow Sea Sand Snails, Stimpson’s Ghost Crabs, and Surf Clams live in sand flats with relatively large particles, and waterbirds are the top predator. Likewise, an unique community evolution appears in Getbol, Korean Tidal Flats, depending on the habitat.
-
- Getbol, Korean Tidal Flats with ecosystem linking of diverse habitats
-
The diverse habitats formed around the island has relatively short distances between habitats, so there are organisms like waterbirds that move between sandy flats and mudflats. This means in the various habitats on different substrates, biotic communities are interconnected.
-
- Why is species diversity so high?! Efficient habitat space
-
All animals need oxygen, even benthic organisms that live in tidal flats. Getbol, Korean Tidal Flats has a thicker oxygen-containing zone (oxidized layer) than other tidal flats around the world, providing a wider habitat for biological species. In addition, each biological species habitat depending on their burrowing ability. If the tidal flats in other countries are like ordinary houses, Getbol, Korean Tidal Flats are like apartments, for compared to the same area it shows high species diversity.